ACIST HDi
HD-IVUSシステム
ACIST HDi HD-IVUSシステム
インターベンション治療に役立つ血管内イメージング画像を提供します。
Kodama®カテーテル
迅速な計測や解析が可能です。またコンパクトに設計されたコンソールはセットアップも容易です。
高いデリバリー性能を発揮します。
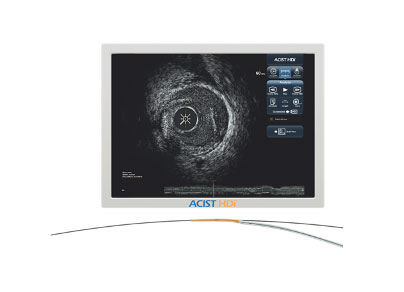

ACIST HDi HD-IVUSシステムでより明確な画像の提供
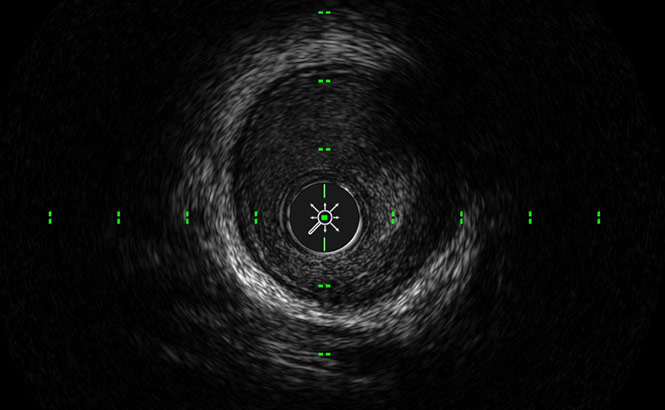
LumenView™
との境界を容易に検出します。
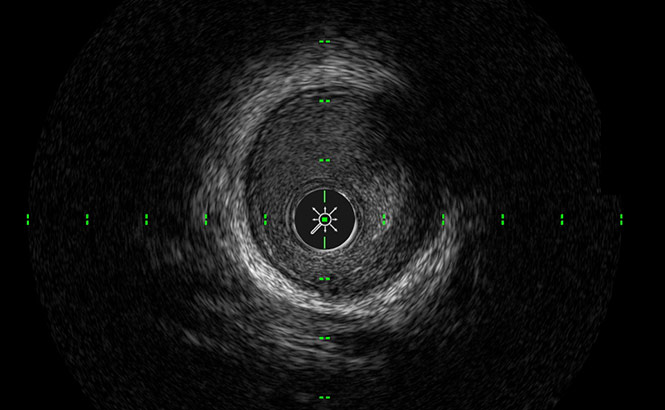
SilkView™
球輝度、組織、およびプラークの識別
が可能となります。
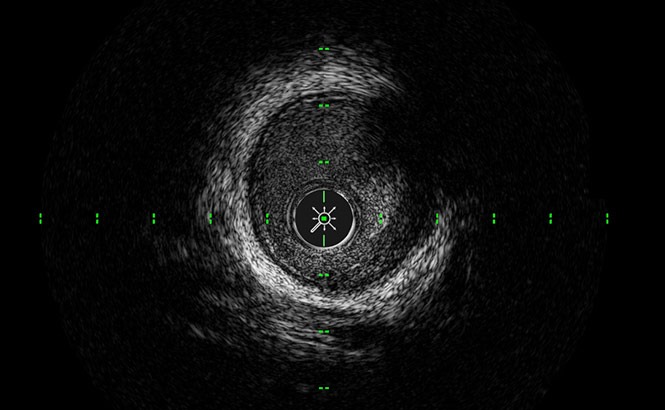
ClassicView™
し、血管内のイメージングが可能とな
ります。
冠動脈IVUS
臨床エビデンス
OCTと比較して、より明確に中膜層を可視化することが可能。⁴

IVUSは74%の症例で治療方針の変更に影響を与えました。⁶
IVUSガイド下のステントでは、Angioガイド下と比較して、 ステント両端のプラーク量が少なく、より大きいMSAが得られた。⁷

40MHzに比べて60MHzでは8倍の 脂質プールの検出が可能8
IVUSガイド下のPCIは、血管造影のみの場合と比較して、びまん性プラーク病変を有する症例のステントエッジ再狭窄の防止に有効です9
末梢血管IVUS
臨床エビデンス

末梢血管インターベンション治療において、IVUSガイドにより術後の合併症や切断リスクが低減11

IVUSを用いたアテレクトミー手技はAngioのみと比較して1年後の血行再建率は2.8倍減少12
血管径の測定値に関して、Angioは一貫してIVUSより小さい結果13
同一病変においてIVUSはAngioに比べて石灰化を69%以上多く検出14
IVUSはAngioと比較して2倍以上の血栓を特定15
IVUSにより確認できたステント留置後の血管内解離は、Angioに比べて4倍以上多かった16
手技中の解離は、IVUSを用いることによりAngioよりも3.5倍以上多く確認17
アテレクトミー後の解離は6倍以上多く確認17
製品紹介ビデオ
引用元
- Data on file – TR-07057 – Internal testing
- Data on file – TR-4050 – Study Summary for Kodama Catheter performance
- Data on file – TR-07057 – Internal testing
- IVUS-Guided Versus OCT-Guided Coronary Stent Implantation: A Critical Appraisal https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcmg.2017.09.008
- Defining a new standard for IVUS optimized drug eluding stent implantation: the PRAVIO study. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. August 1, 2009;74(2):348-356. 6. Maehara A, et al – 16 Nov 2018https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCINTERVENTIONS.117.006243Circulation: Cardiovascular Interventions. 2018;11:e006243
- https://www.tctmd.com/news/ultimate-ivus-superior-angiography-guiding-pci-less-tvf-1-year. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2018.09.01 8. Tanaka S, Sakamoto K, Kitahara H, et al. Assessments of lipid plaque and thrombus with a novel high-definition 60-MHz IVUS imaging system: comparison with conventional 40-MHz IVUS and OCT. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;62(18_S1):B201-B202 8a. Total of 50 matched cross-sections were analyzed with lipid core identified in 8 cross-sections in an ex-vivo study.
- Impact of the distance from the stent edge to the residual plaque on edge restenosis following DES implantation. PLOS One. 2015;10(3):E0121079. 10. Alberti, A., Giudice, P., Gelera, A. et al. Understanding the economic impact of intravascular ultrasound (IVUS). Eur J Health Econ 17, 185–193 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10198-015-0670-4
- Panaich, S. S., Arora, S., Patel, N., Patel, N. J., Savani, C., Patel, A., … Badheka, A. O. (2016). Intravascular Ultrasound in Lower Extremity Peripheral Vascular Interventions: Variation in Utilization and Impact on In-Hospital Outcomes From the Nationwide Inpatient Sample (2006–2011). Journal of Endovascular Therapy, 23(1), 65–75. https://doi.org/10.1177/1526602815620780
- Krishnan, P., Tarricone, A., K-Raman, P., Majeed, F., Kapur, V., Gujja, K., … Sharma, S. (2018). Intravascular ultrasound guided directional atherectomy versus directional atherectomy guided by angiography for the treatment of femoropopliteal in-stent restenosis. Therapeutic advances in cardiovascular disease, 12(1), 17–22. doi:10.1177/1753944717745509
- Pliagas, G., Saab, F., Stavroulakis, K., Bisdas, T., Finton, S., Heaney, C., … Mustapha, J. A. (2020). Intravascular Ultrasound Imaging Versus Digital Subtraction Angiography in Patients With Peripheral Vascular Disease. The Journal of Invasive Cardiology, 32(3), 99–103. Retrieved from https://www.invasivecardiology.com/articles/intravascular- ultrasound-imaging-versus-digital-subtraction-angiography-patients-peripheral-vascular-disease?fbclid=IwAR1qh_GQ85jMvJqGpOeYU_So2gaYF7ol5sknbJmoO-GMmB8JjvMd7gscSi0
- Yin D et al. Intravascular Ultrasound validation of contemporary angiographic scores evaluting the severity of calcification in peripheral arteries. J Endovasc Ther 2017; 24:478-87. 15. Shammas et al. Dethrombosis of the lower extremety arteries using the power-pulse spray technique in patients…. J Endovasc Ther 2008;15:570-79. 16. Miki K, Fujii K, Fukunaga M, et al. Impact of post-procedural intravascular ultrasound findings on long-term results following self-expanding nitinol stenting in superficial femoral artery lesions. Circ J 2013; 77:1543-1550. 17. Shammas NW, Torey JT, Shammas WJ, Jones-Miller S, Shammas GA. Intravascular ultrasound assessment and correlation with angiographic findings demonstrating femoropopliteal arterial dissections post atherectomy: results from the iDissection study. J Invasive Cardiol. 2018;30:240–244.
- Krishnan, P., Tarricone, A., K-Raman, P., Majeed, F., Kapur, V., Gujja, K., … Sharma, S. (2018). Intravascular ultrasound guided directional atherectomy versus directional atherectomy guided by angiography for the treatment of femoropopliteal in-stent restenosis. Therapeutic advances in cardiovascular disease, 12(1), 17–22. doi:10.1177/1753944717745509
- Pliagas, G., Saab, F., Stavroulakis, K., Bisdas, T., Finton, S., Heaney, C., … Mustapha, J. A. (2020). Intravascular Ultrasound Imaging Versus Digital Subtraction Angiography in Patients With Peripheral Vascular Disease. The Journal of Invasive Cardiology, 32(3), 99–103. Retrieved from https://www.invasivecardiology.com/articles/intravascular-t sound-imaging-versus-digital-subtraction-angiogra phy-patients-peripheral-vascular-disease?fbclid=IwAR1qh_GQ85jMvJqGpOeYU_So2gaYF7ol5sknbJmoO-GMmB8JjvMd7gscSi0
- Yin D et al. Intravascular Ultrasound validation of contemporary angiographic scores evaluting the severity of calcification in peripheral arteries. J Endovasc Ther 2017; 24:478-87.
- Shammas et al. Dethrombosis of the lower extremety arteries using the power-pulse spray technique in patients…. J Endovasc Ther 2008;15:570-79.
- Miki K, Fujii K, Fukunaga M, et al. Impact of post-procedural intravascular ultrasound findings on long-term results following self-expanding nitinol stenting in superficial femoral artery lesions. Circ J 2013; 77:1543-1550.
- Shammas NW, Torey JT, Shammas WJ, Jones-Miller S, Shammas GA. Intravascular ultrasound assessment and correlation with angiographic findings demonstrating femoropopliteal arterial dissections post atherectomy: results from the iDissection study. J Invasive Cardiol. 2018;30:240–244.’ 8. Data on file – TR-07057 – Internal testing. 9. Data on file – TR-4050 – Study Summary for Kodama Catheter performance.
HDiシステムのご使用にあたり、「取扱説明書」を必ずお読みください。
使用上の注意:
HDiシステムは、心血管及び末梢血管内の超音波検査に使用することを目的としています。血管内超音波イメージングは、経皮的インターベンションを受けられる患者様に適応されます。Kodamaカテーテルは、HDiシステムとの使用を目的としています。
禁忌:
菌血症又は敗血症、血管攣縮、血液凝固系異常、機械的人工心臓弁が留置されており、重篤な血行動態的不安定、又はショック、完全閉塞、脳血管系での使用は禁忌です。
安全性についての重要情報:
HDiシステムは、医師の指示のもとで血管造影時の手技・治療において十分なトレーニングと経験を積んだ医療従事者のみが操作・使用するものとします。Kodama カテーテルはショートモノレールシステムを採用しています。そのため、カテーテルの着脱時にガイドワイヤーが絡まったり、離脱することがあります。使用前及び使用中には、Kodamaカテーテルにキンクやその他の損傷の有無を確認してください。 キンクや破損したカテーテルは、血管の損傷やカテーテル操作ができなくなることがあるので使用しないでください。
抵抗を感じた場合は、X線で抵抗の原因を特定するまでは絶対に抵抗に逆らってKodamaカテーテルを前進又は後退させないでください。 抵抗に逆らってカテーテルやガイドワイヤーを動かすと、カテーテルやガイドワイヤー先端の伸長や分離、損傷、血管の穿孔が生じる場合があります。ステントが留置されている血管にKodamaカテーテルを挿入する際は、ショートモノレールシステムがガイドワイヤーやカテーテルに絡まったり、カテーテル先端の剥離、ステントの移動などが起こりやすくなりますので十分注意して使用してください。
血管内超音波イメージングに起こりうる有害事象には以下が含まれます。血管閉塞、空気塞栓症、動脈の解離、損傷、穿孔、急性心筋梗塞、心室性頻拍、心室細動、完全房室ブロックを含むこれらに限定されない不整脈、心タンポナーデ、カテーテル/ガイドワイヤーのエントラップメント、カテーテル誘発による虚血発作、死亡、血管形成術/ステントを含むインターベンション治療を必要とする血管損傷、感染症、ステントストラットの損傷、脳卒中(脳血管障害及び一過性脳虚血発作を含む)、血栓形成又は血栓塞栓症、血管攣縮などがありますが、これらに限定されません。


